Key Components of Nutrition
Macronutrients: Proteins, Fats, and Carbohydrates
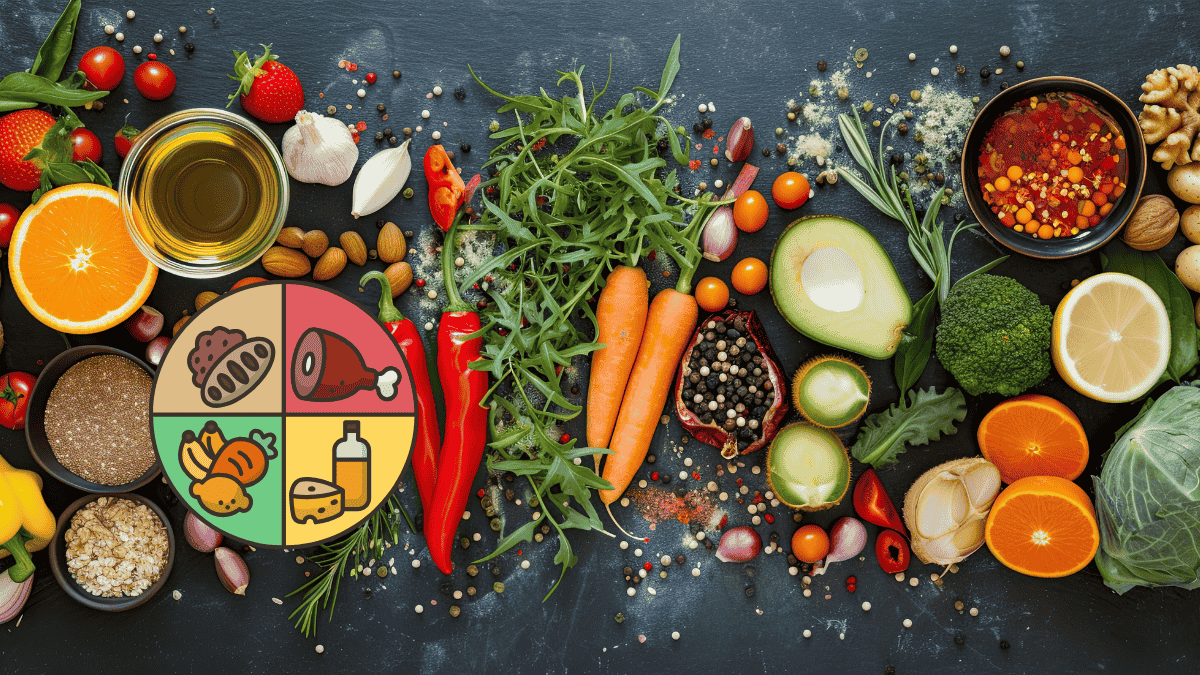
Macronutrients are the building blocks of our diet, providing the energy necessary for our bodies to function. They consist of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, each playing a unique and vital role.
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, making them crucial for growth and maintenance. They can be found in various sources, from animal products like meat and dairy to plant-based options such as legumes and nuts.
Fats, often misunderstood, are equally important. They come in different types, including saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are vital for brain health, hormone production, and absorbing certain vitamins.
Carbohydrates serve as the body’s primary energy source. Carbohydrates can be divided into two categories: simple carbs and complex carbs.While simple carbohydrates, like sugars, provide quick energy, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains and vegetables, offer sustained energy and important nutrients.
Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals
Micronutrients, though needed in smaller amounts, are essential for maintaining overall health. They include vitamins and minerals that support numerous bodily functions.
Vitamins can be classified into two types: water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins. Water-soluble vitamins, like Vitamin C and various B vitamins, play crucial roles in energy production and immune function. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as Vitamins A, D, E, and K, are important for vision, bone health, and blood clotting.
Minerals, on the other hand, are inorganic substances vital for processes like bone formation, nerve transmission, and muscle function. Key minerals include calcium, which is essential for bone health, iron for transporting oxygen in the blood, and potassium for maintaining fluid balance.
Water: The Forgotten Nutrient
Water, often overlooked, is perhaps the most vital nutrient of all. It plays a critical role in nearly every bodily function, including digestion, circulation, temperature regulation, and waste elimination.
Maintaining proper hydration is essential for optimal health. Dehydration can lead to a variety of issues, from fatigue and headaches to more serious health concerns.
Daily water needs can vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and climate, but a good rule of thumb is to drink water consistently throughout the day.
Incorporating a balance of macronutrients, micronutrients, and adequate hydration is key to achieving a well-rounded diet that supports overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Nutrition for Health
Role of Nutrition in Growth and Development
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in growth and development, especially during critical life stages such as infancy, childhood, and adolescence. During these periods, the body requires a variety of nutrients to support rapid growth, development of organs, and overall health.
Adequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, proteins, and healthy fats is crucial for building strong bones, developing muscle mass, and supporting cognitive function. For example, calcium and vitamin D are vital for bone health, while iron is essential for cognitive development and energy levels. A balanced diet during these formative years not only fosters physical health but also sets the stage for lifelong habits and wellness.
Nutrition’s Impact on Immune Function
The link between nutrition and immune function is profound. A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can enhance the body’s immune response. Specific nutrients, such as vitamins A, C, D, and E, as well as minerals like zinc and selenium, are known to support immune health by helping to produce immune cells and antioxidants that combat oxidative stress.
Conversely, poor nutrition can lead to a weakened immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Adequate nutrition not only helps prevent diseases but also plays a role in recovery, allowing the body to heal more efficiently when faced with health challenges.
How Nutrition Affects Mental Health
Nutrition significantly influences mental health, impacting mood, cognitive function, and overall emotional well-being.
Research has shown that certain nutrients can affect neurotransmitter function, which plays a critical role in regulating mood and mental clarity.

For instance, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish are associated with reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Moreover, a diet rich in whole foods—such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins—can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce mood swings. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats may contribute to increased anxiety and depression.
Common Nutritional Deficiencies
Signs and Symptoms of Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can occur when the body lacks essential vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients needed for optimal health. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of these deficiencies is crucial for early intervention and treatment.
For instance, a deficiency in vitamin D can lead to fatigue, bone pain, and muscle weakness, while insufficient iron may result in anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause neurological issues, including numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, as well as cognitive disturbances. Additionally, a lack of calcium can manifest as brittle bones and dental problems.
Other deficiencies, such as vitamin C, may present with symptoms like frequent infections, slow wound healing, and easy bruising. By being aware of these signs, individuals can seek medical advice and adjust their diets to prevent long-term health issues.
How to Address Nutritional Gaps
Addressing nutritional gaps involves a combination of dietary changes, supplementation, and lifestyle modifications. The first step is to assess one’s diet and identify areas lacking in essential nutrients. Keeping a food diary can be a helpful tool in understanding dietary patterns and pinpointing deficiencies.
Incorporating a variety of whole foods—fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats—into daily meals is key to achieving a balanced nutrient intake. For example, to boost iron levels, one might include more lean meats, legumes, and dark leafy greens. To enhance calcium intake, incorporating dairy products or fortified alternatives can be beneficial.
In some cases, dietary changes alone may not suffice, and supplementation may be necessary. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help determine the right supplements and dosages based on individual needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nutrition is a vital cornerstone of health that influences every aspect of our well-being. By understanding the significance of a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, individuals can make informed choices that promote optimal health, prevent chronic diseases, and enhance overall quality of life.
Prioritizing nutrition is not just about fueling the body; it’s about fostering long-term wellness and resilience. Embracing healthy eating habits empowers us to thrive physically, mentally, and emotionally, ultimately leading to a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
FAQs
What is nutrition?
Nutrition is the science of how food affects our health and well-being.
Why is nutrition important?
Proper nutrition supports growth, immune function, energy production, and disease prevention.
What are essential nutrients?
Essential nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals needed for bodily functions.
How can I improve my nutrition?
Focus on a balanced diet with a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Can nutrition affect mental health?
Yes, a well-balanced diet can positively impact mood and cognitive function.